AWS Availability Zones
AWS Availability Zones (AZs) are a core concept of AWS cloud architecture.
They exist to make sure your application remains available, reliable, and fault-tolerant, even when something goes wrong.
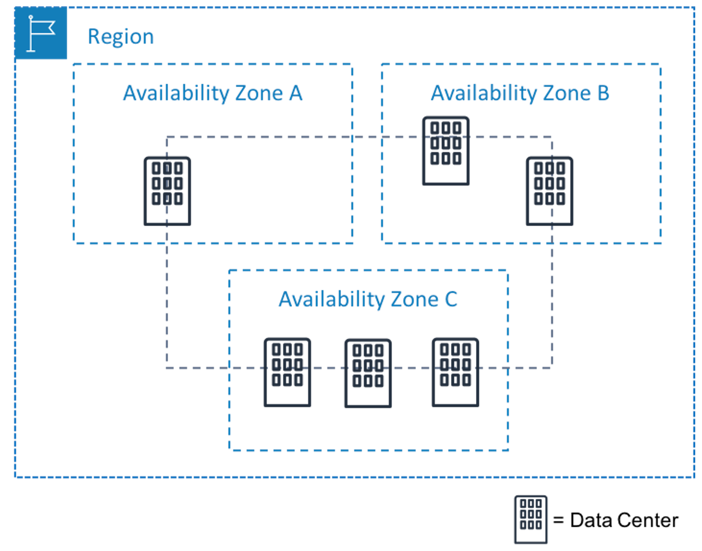
An Availability Zone is one or more physically separate data centers inside an AWS Region.
Each AZ has its own power, networking, cooling, and security, which means a failure in one AZ does not affect the others.
In Simple Words
Availability Zones are separate safe rooms inside a region. If one room catches fire, the others keep working.
Why AWS Introduced Availability Zones
In real life, failures are unavoidable:
- Power outages happen
- Hardware fails
- Network links break
In traditional hosting:
- One data center fails
- Entire website goes down
AWS designed Availability Zones so that:
- Applications don’t depend on a single data center
- Failures are isolated
- Users stay connected
Core Idea
AWS does not try to avoid failure. AWS designs systems to survive failure.
Relationship Between Region and Availability Zones
- Region → A large geographic area (example: Mumbai)
- Availability Zone → Independent data centers inside that region
Each region contains:
- At least 2 Availability Zones
- Usually 3 or more Availability Zones
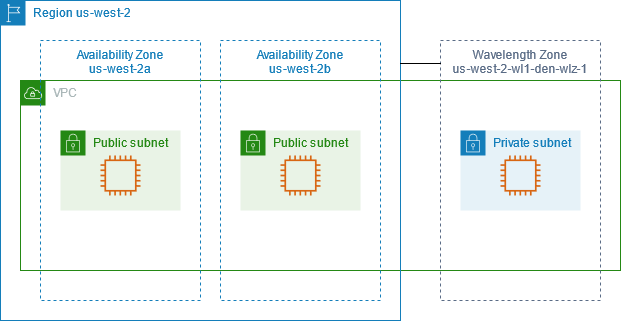
These AZs are connected using high-speed private networks, allowing fast and secure communication.
Important
High availability in AWS is achieved by using multiple AZs, not by using a single powerful server.
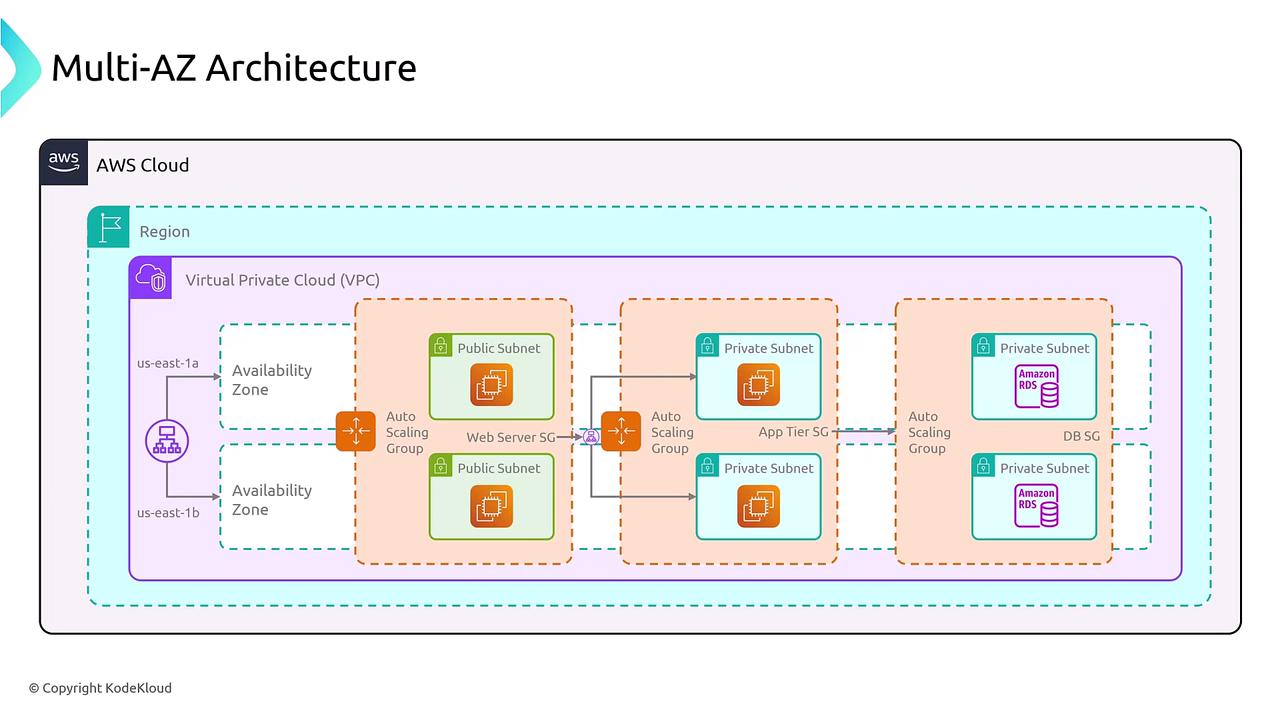
How Availability Zones Protect Your Application
When an application is deployed across multiple AZs:
- Traffic is distributed between zones
- If one AZ goes down, traffic is routed to healthy AZs
- Users experience no downtime
This happens automatically when AWS services are configured correctly.
Simple Example
Your website runs in 3 AZs. 1 AZ fails → 2 AZs continue serving users → website stays online.
Single AZ vs Multi-AZ (Easy Comparison)
Single Availability Zone
- Easy to set up
- High risk
- Not suitable for production
Multiple Availability Zones
- Highly available
- Fault tolerant
- Used by real-world applications
Beginner Mistake
Deploying everything in one AZ creates a single point of failure.
Availability Zones in Real AWS Services
Many AWS services are designed around AZs:
- Load Balancers distribute traffic across AZs
- Auto Scaling launches servers in multiple AZs
- Databases support Multi-AZ failover
You don’t need to manage failures manually.
AWS handles it for you.
Key Benefit
Availability Zones make high availability simple and practical.
Why Availability Zones Matter for You
Understanding AZs helps you:
- Build production-ready applications
- Design fault-tolerant systems
- Understand AWS architecture deeply
- Clear AWS interviews and certifications
Learning Insight
If Regions explain where AWS is, Availability Zones explain how AWS stays online.
Quick Exercise
- Open AWS Console
- Select any region
- Create a resource and notice the Availability Zone options
- Think: “What happens if this AZ fails?”