AWS Regions
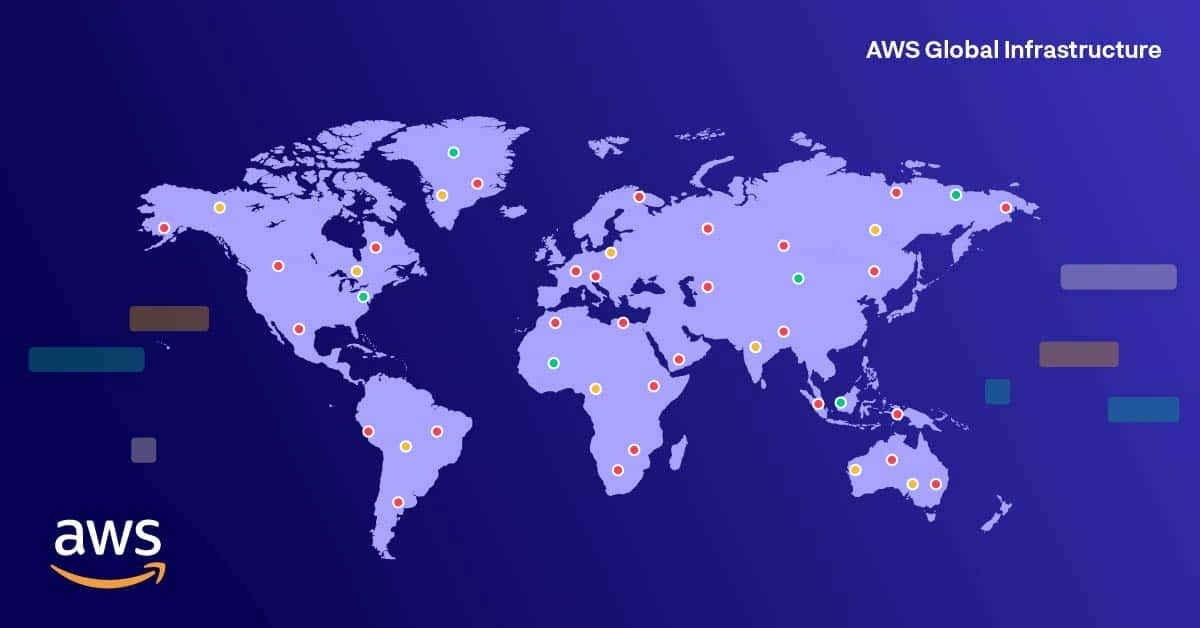
AWS Regions are geographically separate locations around the world where Amazon Web Services operates its cloud infrastructure.
Each region is designed to be isolated, secure, and highly available, allowing applications to run closer to users with low latency and high reliability.
Goal of This Lesson
By the end of this article, you will understand:
- What AWS Regions are in detail
- Why AWS has so many regions worldwide
- How regions affect performance, security, and cost
- A complete overview of AWS Regions across the globe
Simple Definition
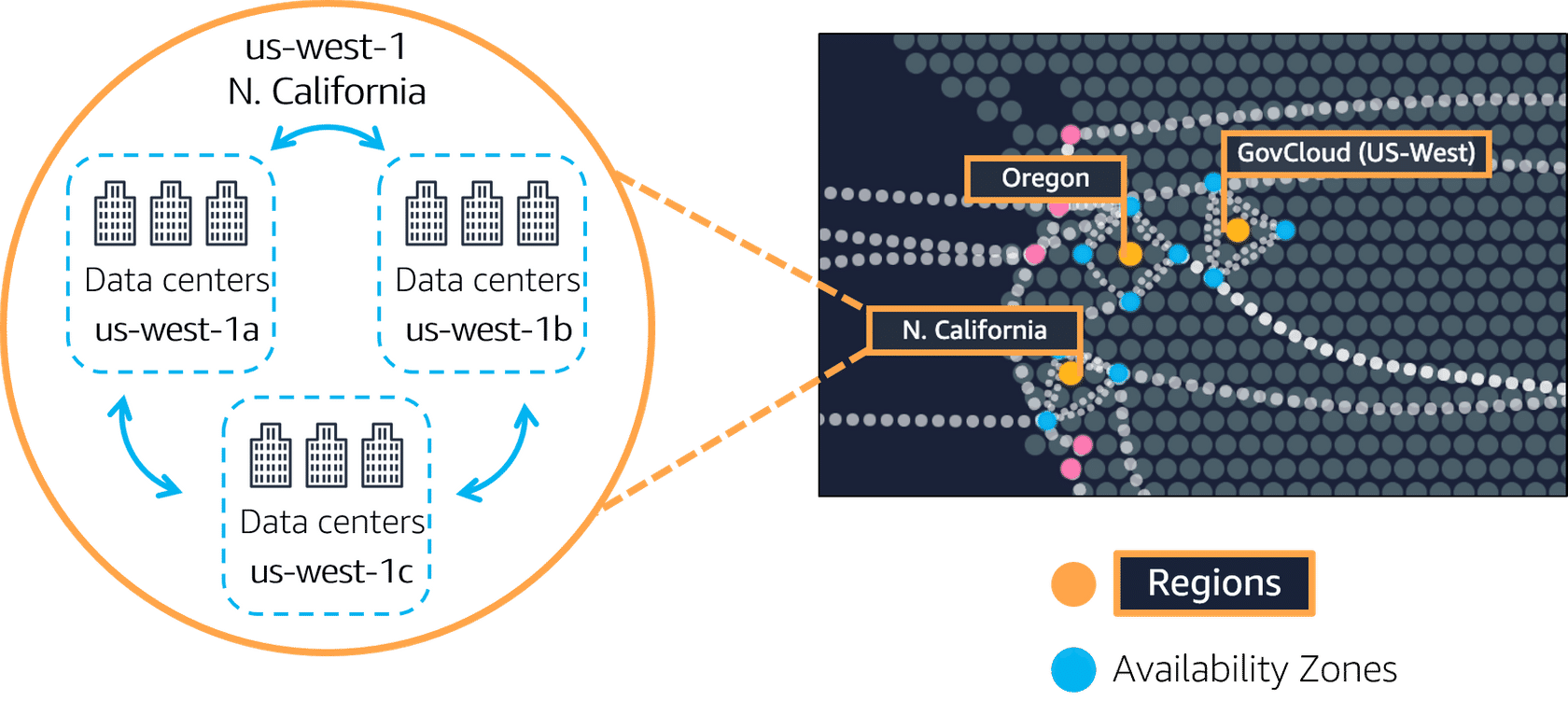
An AWS Region is a physical location in the world that contains multiple data centers called Availability Zones.
Why AWS Regions Exist
Users are spread across the globe.
If an application hosted in one country is accessed from another country far away, users experience slow response times.
AWS Regions solve this by:
- Hosting applications close to end users
- Reducing network latency
- Improving user experience
- Meeting country-specific data laws
Pro Tip
Lower distance between users and servers means faster applications.
A Short Story: Region Choice Gone Wrong
A company hosted its entire application in a single region far from its users.
What happened:
- Website loaded slowly
- Payments timed out
- Users abandoned the app
After moving the application to a nearby AWS Region:
- Page load time dropped
- Conversion rate improved
- Customer complaints reduced
Lesson Learned
Choosing the right AWS Region directly impacts business success.
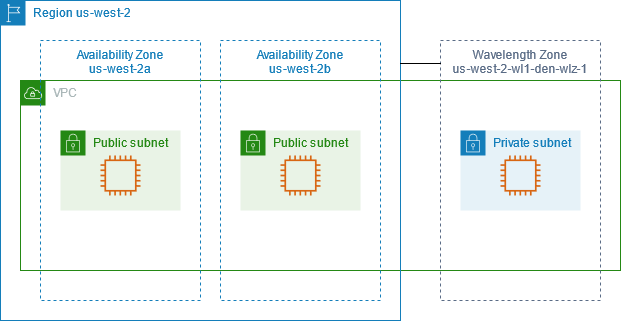
What Is Inside an AWS Region?
Each AWS Region contains:
- Multiple Availability Zones (AZs)
- Separate power supply and networking
- Independent failure domains
- High-speed private connections between AZs
This design ensures:
- High availability
- Fault tolerance
- Disaster recovery readiness
Real World Scenario
If one data center fails due to power issues, the application continues running from another Availability Zone in the same region.
AWS Regions vs Availability Zones
- Region: Large geographic area (example: Mumbai)
- Availability Zone: One or more data centers inside a region
Important
Best practice is to deploy applications across multiple Availability Zones within a region.
How AWS Regions Help During Peak Events
During high-traffic events like sales or launches:
- Millions of users access the app simultaneously
- Systems must stay responsive
- Downtime is unacceptable
AWS Regions help by:
- Supporting local scaling
- Isolating failures
- Maintaining uptime under heavy load
Result
Applications remain fast, stable, and available even under extreme traffic.
AWS Regions Around the World (Table)
| Continent | AWS Region Name | Region Code |
|---|---|---|
| North America | US East (N. Virginia) | us-east-1 |
| North America | US East (Ohio) | us-east-2 |
| North America | US West (N. California) | us-west-1 |
| North America | US West (Oregon) | us-west-2 |
| South America | São Paulo | sa-east-1 |
| Europe | Ireland | eu-west-1 |
| Europe | London | eu-west-2 |
| Europe | Frankfurt | eu-central-1 |
| Europe | Paris | eu-west-3 |
| Europe | Milan | eu-south-1 |
| Europe | Stockholm | eu-north-1 |
| Middle East | UAE (Abu Dhabi) | me-central-1 |
| Middle East | Israel (Tel Aviv) | il-central-1 |
| Asia Pacific | Mumbai | ap-south-1 |
| Asia Pacific | Hyderabad | ap-south-2 |
| Asia Pacific | Singapore | ap-southeast-1 |
| Asia Pacific | Sydney | ap-southeast-2 |
| Asia Pacific | Tokyo | ap-northeast-1 |
| Asia Pacific | Seoul | ap-northeast-2 |
| Asia Pacific | Hong Kong | ap-east-1 |
| Asia Pacific | Jakarta | ap-southeast-3 |
| Asia Pacific | Melbourne | ap-southeast-4 |
| Africa | Cape Town | af-south-1 |
| China | Beijing | cn-north-1 |
| China | Ningxia | cn-northwest-1 |
Region Expansion
AWS continuously launches new regions to meet global demand.
Choosing the Right AWS Region
While selecting a region, consider:
- Location of users
- Data residency laws
- Service availability
- Cost differences
- Disaster recovery strategy
Caution
Some AWS services or features may not be available in every region.
Why AWS Regions Matter for Your Career
Understanding regions helps you:
- Design global applications
- Build highly available systems
- Optimize cost and performance
- Prepare for real-world cloud architectures
Learning Insight
AWS Regions form the base layer of all AWS architecture decisions.
Exercise
- Log in to the AWS Console
- Switch between at least three regions
Observe:
- Available services
- Region-specific differences
- Default region behavior